You’re not buying a kitchen composter because you love appliances. You’re buying it because your trash can smells like a crime scene by day two, and you’re tired of carrying wet scraps outside like a sad raccoon. So, let’s do this properly.
This is a buyer-first comparison between GEME Terra II and Reencle Prime—two microbial composters (yes, Reencle is microbial). The real difference is: Which one fits your life with less effort, less refills, and fewer “why is it wet?” moments.
If you want the short answer: most households should buy Terra II because it’s built around higher daily capacity and lower maintenance, and that’s what makes people actually keep using a composter.
The 90-Second Truth
1. Output expectation matters more than speed
Two machines can reduce volume quickly, but still produce very different “end states” (finished compost vs. partially stabilized residue that benefits from curing).
2. Daily capacity and routine should match your kitchen
Reencle commonly recommends an optimal daily input of ~0.7 kg (max ~1.0 kg), whereas GEME Terra II's max daily input can be up to ~2.0 kg. If your household produces more scraps, “continuous handling” and capacity become decision drivers.
3. Maintenance isn’t just cleaning, it’s consumables
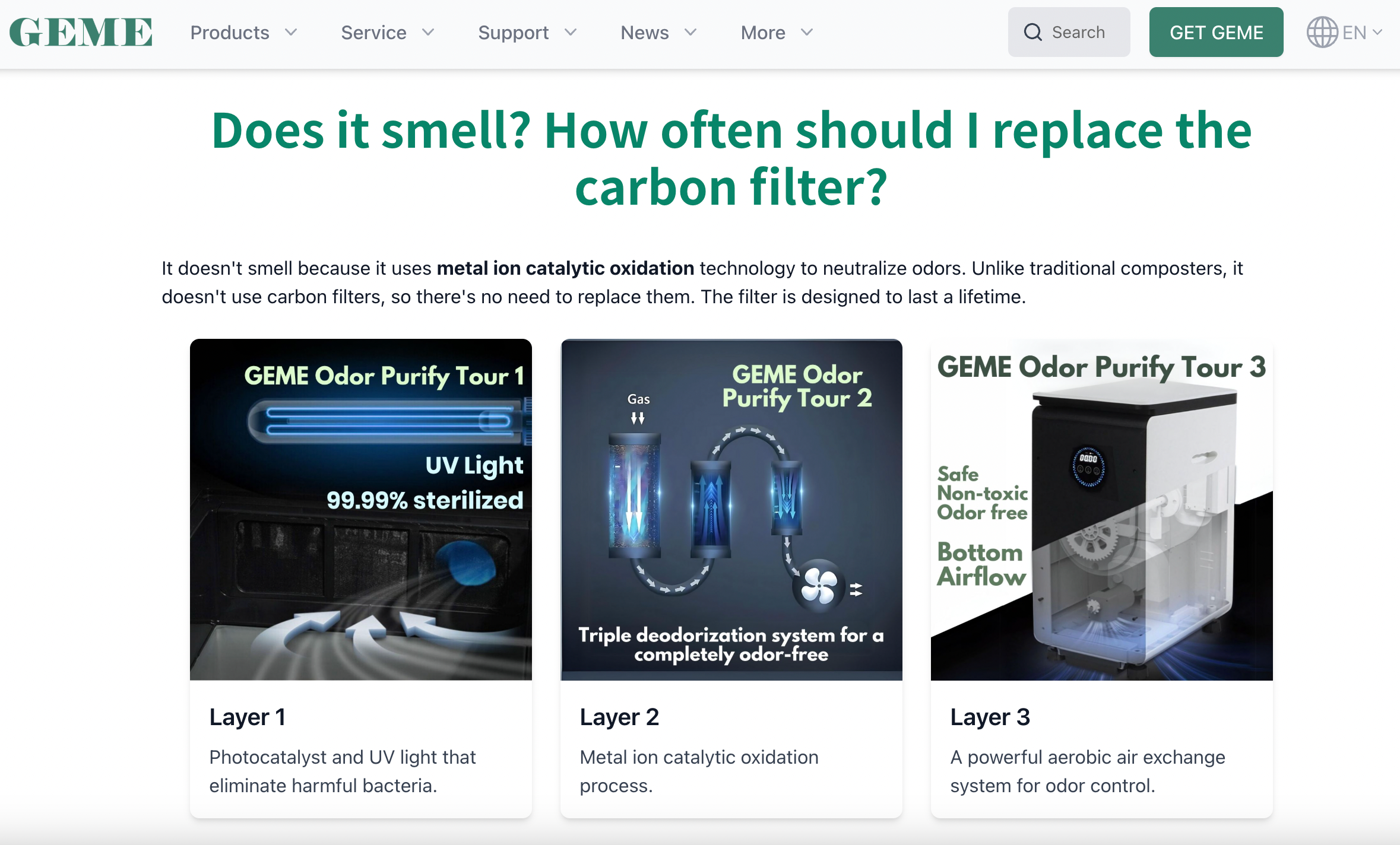
Reencle documentation commonly recommends carbon filter replacement every ~9–12 months, depending on use. (For any brand, ongoing costs add up and should be evaluated as TCO.) GEME Terra II doesn't have any ongoing consumables.
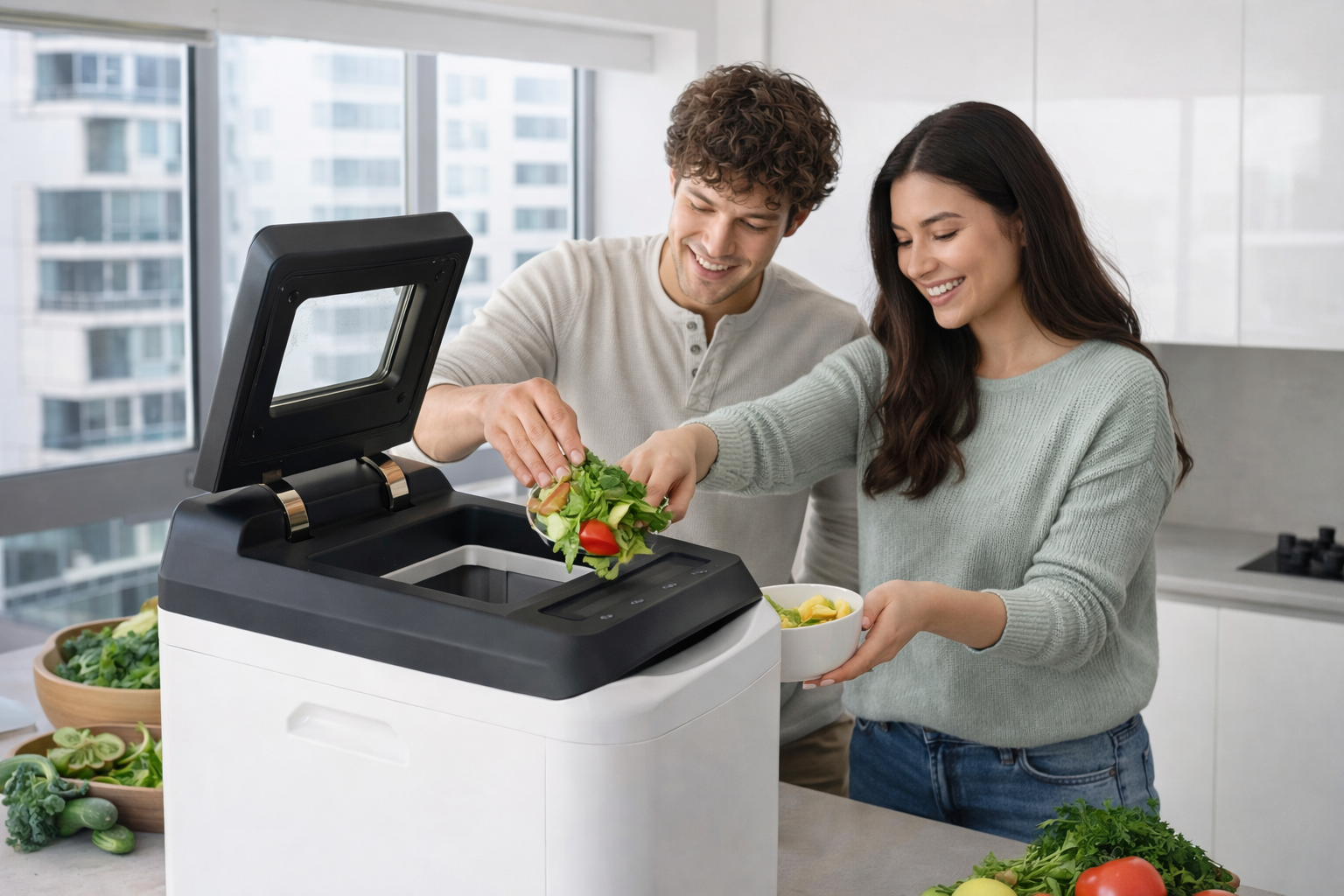
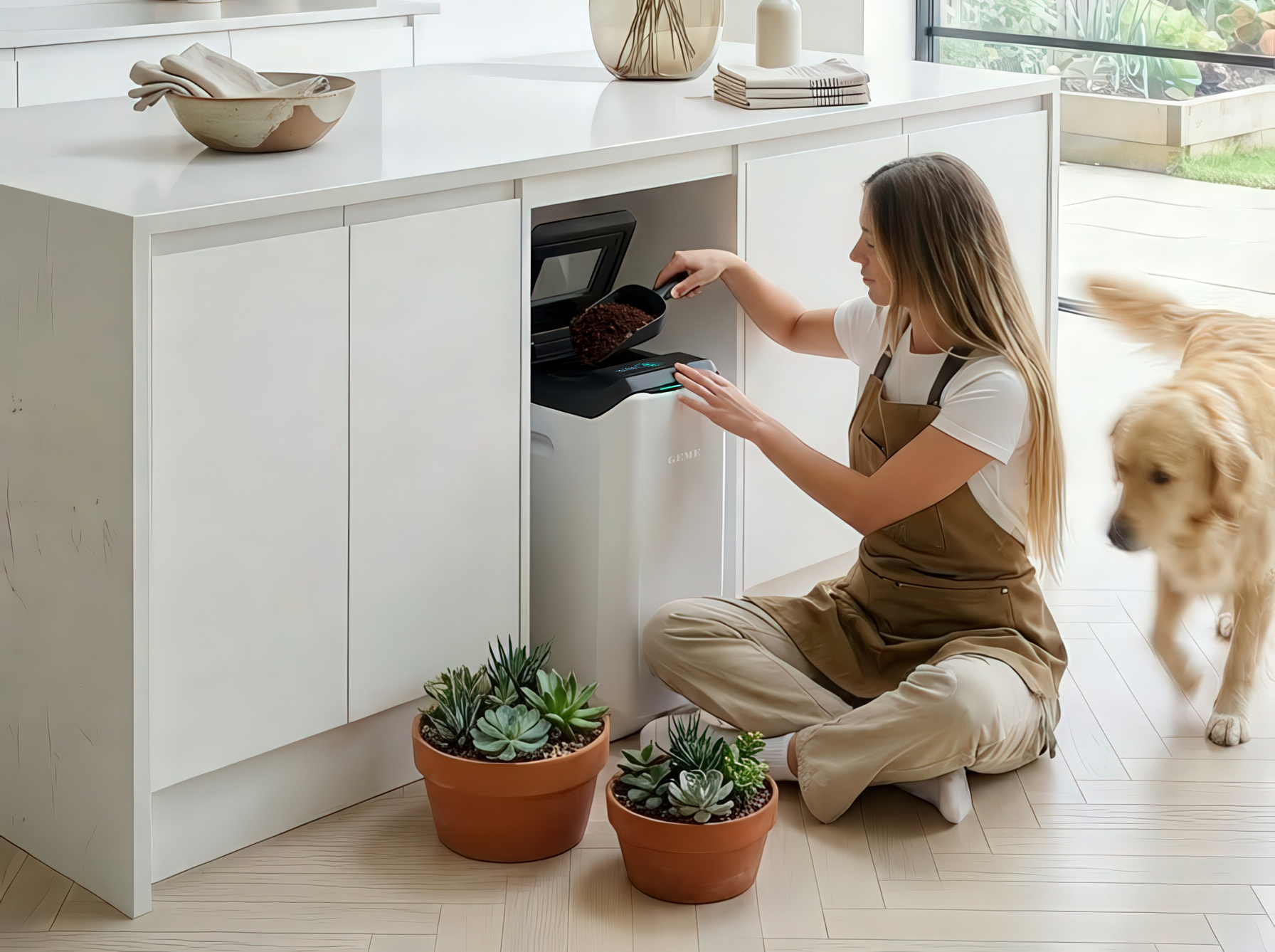






 Image: Modern indoor composting – even with a convenient countertop bin, hidden costs like filter replacements can add up over time.
Image: Modern indoor composting – even with a convenient countertop bin, hidden costs like filter replacements can add up over time.